Main Article Content
Abstract
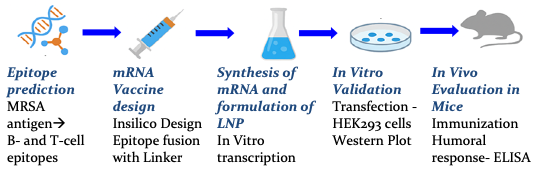
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections represent a critical healthcare challenge. In this study, we describe the design a multi-epitope mRNA vaccine encoding immunodominant MRSA antigens, delivered using a novel lipid nanoparticle system. Preclinical evaluation in murine models demonstrated robust humoral and cellular immune responses, with significant protection against MRSA challenge. The vaccine exhibited excellent safety and tolerability profiles. No bacterial colonies were detected in the brain, lung, and spleen tissues of the mice that were immunized with the mRNA vaccine at dosages of 75, 150, or 300 µg. No statistical difference in bacterial burden was found among the mRNA-dosed groups. Our findings support the further development of mRNA-based strategies for combating antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections.
Keywords
Article Details
Copyright (c) 2025 Noor Z. Kbah , Fatemah Hasan Shkir, Saja Hussein Hashim , Qassim A. Zigam, Ahmed R. Ali (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.